SQL: ODBC Task
Disclaimer
Your use of this download is governed by Stonebranch’s Terms of Use, which are available at Stonebranch Integration Hub - Terms of Use.
Overview
This Universal Extension provides the capability to integrate with ODBC-compliant database, by running single or multiple SQL commands and retrieving the resulting data. While it is designed to work with any ODBC-compliant database, it is thoroughly tested against MySQL, MSSQL Server, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SAP HANA, and Amazon Redshift databases.
As opposed to the native UAC SQL Task, which runs on the Controller, this integration allows the user to run an SQL ODBC Task from the Agent.
Version Information
Template Name | Extension Name | Extension Version | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
SQL ODBC | ue-sql-odbc | 3.0.1 | Fixes and new Features are introduced. |
SQL ODBC 3.0.0 is a major release update and introduces breaking changes that might affect some customers depending on their setup. Administrators are strongly advised to refer to Changelog for more information on the changes introduced if updating from a version earlier than 3.0.0
Key Features
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Support ODBC-compatible databases | The interaction with the supported databases is based on ODBC API and the non-vendor-specific Python library “pyodbc”. This translates to support for every database that is compatible with this API and has a corresponding ODBC driver. The extension is explicitly tested for MySQL 8.0, MSSQL Server 16.0, PostgreSQL 12.15, Oracle 21c Express Edition 21.3, and SAP HANA Express Edition 2.0 SPS 06 and serverless Amazon Redshift. |
Connectivity options | Multiple connectivity options available for maximum flexibility:
|
Support of SQL scripts | Input may contain one or multiple SQL commands, following the syntax of the target database server. |
Automatic database commit or rollback | On successful SQL command execution, the extension commits the result, but if any errors occur a rollback is triggered. |
Multiple options for data output | A task execution can provide the SQL query returned data with any of the following options:
|
Provide SQL execution metadata | The following metadata is provided as part of the Task Instance Extension output.
Rows affected and messages can vary greatly between different databases and drivers. |
Observability | Calculate and expose important metrics related to task executions. |
Software Requirements
This integration requires a Universal Agent and a Python runtime to execute the Universal Task.
Area | Details |
|---|---|
Python Version | Requires Python 3.7 or later, tested with Python 3.7.16 and Python 3.11.6 |
ODBC Drivers | ODBC database drivers installation based on vendor-specific instructions. |
Universal Agent | Both Windows and Linux agents are supported:
|
Universal Controller | Universal Controller Version >= 7.4.0.0 |
Network and Connectivity | Network connectivity to the target database server, from the agent executing the task. |
Database | ODBC-compliant database server. |
Supported Actions
Action: Run SQL Script
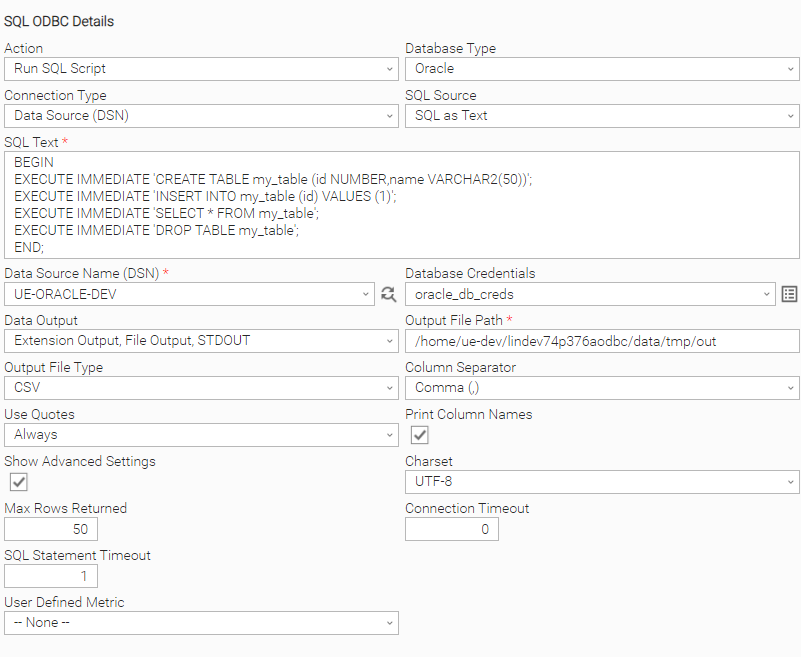
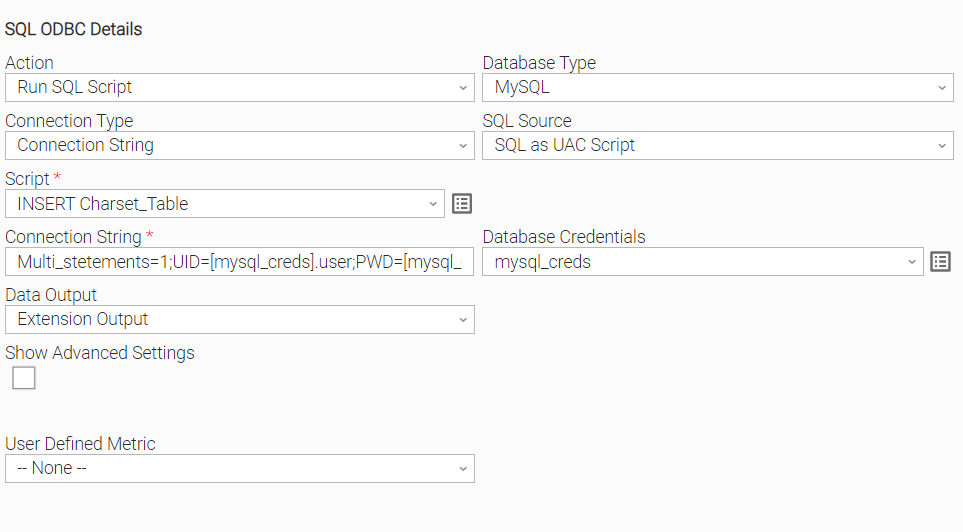
Execute an SQL UAC Script in the selected database. The user is given the option to choose where the output of the Task Instance is to be viewed. A database driver may or may not support the execution of multiple SQL commands. For instance, in MySQL case, the user should specify the “MULTI_STATEMENTS=1” parameter in the connection string in order to be able to run multiple SQL statements, whereas Oracle Database Driver does not support this feature at all, thus multiple SQL commands should be provided in a single PL/SQL block.
Configuration examples
Scenario A: Connect with a DSN file in an Oracle Database. Oracle driver does not support the execution of multiple SQL commands, hence all the SQL commands should be in a PL/SQL block. | Scenario B: Connect with a connection string and execute an SQL Script with multi SQL statements in MySQL Database. MULTI_STATEMENTS=1 is specified in the connection string. UID and PWD are being specified with [credential_name].user and [credential_name].password notation for enhanced security. |
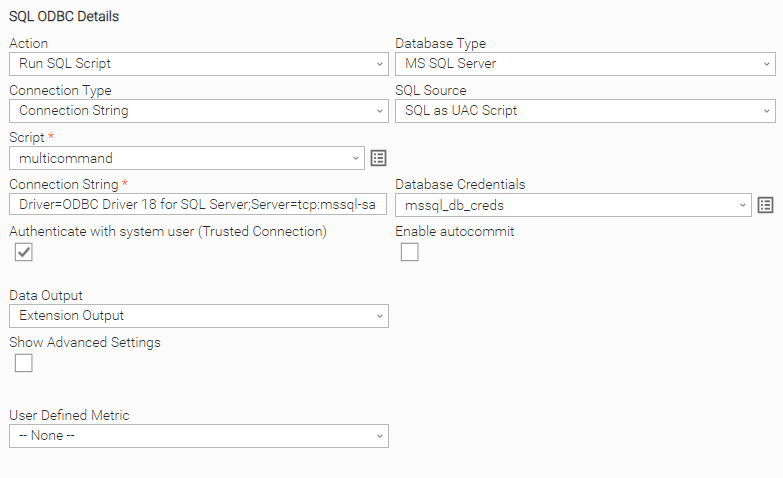
Scenario C: A connection to an MSSQL Server Database can be established using the Trusted Connection feature. When this checkbox is enabled, the need to include the User ID (UID) and Password (PWD) in the connection string can be omitted. Connection String example: Driver=ODBC Driver 18 for SQL Server;Server=tcp:mssql-sample.org:1443;Database=mydb;TRUSTSERVERCERTIFICATE=yes; |
Action Output
Output Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
EXTENSION | Standard Universal Extension format The extension output follows the standard Extension output format, providing:
| |
STDOUT | If STDOUT is selected in the “Data Output“ option, the extension outputs the retrieved data in a human-friendly tabular format. | |
STDERR | The SQL statement executed in the target database is printed when the Universal Extension Task is run with the log level set to DEBUG. |
SQL Script Definition and Guidelines
An SQL script is a file containing a sequence of SQL (Structured Query Language) statements or commands. It is used to perform various operations on a relational database, such as creating tables, inserting data, modifying data, retrieving data, or managing other database-related tasks.
The following guidelines provide recommendations and best practices for writing SQL scripts:
- The extension does not perform any validation on the SQL script. The format of the script strongly relates to the Database and the capabilities of vendor-specific Database ODBC driver.
Commit statements should not be contained inside the script. Commit is explicitly executed only if the execution of the SQL Script is successful as a whole. SQL Script execution is atomic, meaning that if any command fails, or an unexpected error occurs, all the changes, if any, made to the database are rollbacked.
UAC variables can be used to change the content of the SQL script dynamically if required.
Input Fields
Field | Type | Description | Version Information |
|---|---|---|---|
Action | Choice | The action performed upon the task execution. Available actions are as follows:
| Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Database Type | Choice | The database type. The following options are available:
| Introduced in 1.0.0 |
SQL Source | Choice | Defines the source of the SQL Script:
| Introduced in 2.1.0 |
Script | Script field | UAC script that contains the SQL command(s). Required & visible only when field SQL Source= “SQL as UAC Script”. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
SQL Text | Large Text | The SQL commands to be executed. | Introduced in 2.1.0 |
Connection Type | Choice | Different options are possible for the selection of connection parameters. Available options are the following:
| Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Database Credentials | Credentials | Username and Password for connecting to the database. Credentials definition should be as follows:
| Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Authenticate with system user (Trusted Connection) | Checkbox | Check this field in order to use the “trusted connection“ option, when using a Windows agent to connect to an MS SQL Server. Default setting is unchecked. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Enable autocommit | Checkbox | When checked the autocommit mechanism is enabled. When this flag is activated, transactions are automatically committed by the DB server. Consequently, the Universal Task lacks transaction control capability, preventing any rollback action initiated by the task in case of errors from reversing transactions already committed by the server.
Default setting is unchecked. | Introduced in 2.2.0 |
Database Host | Text | The host of the database server. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Database Port | Integer | The port is used to connect to the database server. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Database Name | Text | The name of the database in the target database server. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Database Driver | Dynamic choice | The driver is used for connecting to the database server. It is a dynamic choice field, with the values being retrieved from the system configuration. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Data Source Name (DSN) | Dynamic Choice | The DSN is used for connecting to the target database server. It is a dynamic choice field, with the values being retrieved from the system configuration. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
File Data Source Name (FILEDSN) | Text | The path of the FILEDSN file. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Connection String | Text | The raw connection string that should be used to connect to the target database. Required & visible only when field Connection Type = “Connection String”. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Data Output | Multiple Choice | Data output methods for the SQL data retrieved. Available options are:
Notice: When option “File Output“ is selected and multiple result sets are the result of the SQL script execution (for example multiple SELECT STATEMENTS included in the SQL script), one file is created for each result set. The file naming convention adheres to the sequence file_1, file_2, file_3, etc. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Output File Path | Text | The file that will be used to save the SQL query data. If this does not exist it wit will be created, if it exists it will be truncated prior to being used. The file extension needs to be included. Required & visible only when field Data Output = “File Output”. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Output File Type | Choice | The internal representation of the Output File. Available options are as follows:
Required & visible only when field Data Output = “File Output”. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Column Separator | Choice | The character to be used as a column separator. Available options are as follows:
Required & visible only when field Output File Type = “CSV” | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Use Quotes | Choice | Choose when to use quotes in the CSV output. Available options are as follows:
Required & visible only when field Output File Type = “CSV” | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Print Column Names | Checkbox | Choice to print or not the column names as a first line in the CSV file. Default setting is checked. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Show Advanced Settings | Checkbox | Controls show/hide of the fields that belong to the “Advanced“ section. Default setting is unchecked. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Charset | Choice | Configure the charset to be used when parsing database data retrieved. Selecting the option “Use Default“, the extension will try to use the most commonly used charset for each database type, but you can also override this setting with one of the other options of the list. Available options are as follows:
Visible only when “Advanced“ is selected. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Max Rows Returned | Integer | For the cases where data are produced as a result of the SQL script execution, limit the rows of data returned. Filtering is applied after the SQL script is executed, on the client side, so this is not the same as using the “LIMIT” keyword in your SQL statements. Visible only when “Advanced“ is selected. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Connection Timeout | Integer | Define the number of seconds to wait for establishing the connection to the database server. Value zero (0) disables this timer, with the connection attempt waiting indefinitely. Not supported for all ODBC Drivers. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
SQL Statement Timeout | Integer | Define the number of seconds to wait for the result on an SQL statement executed to the database server. Value zero (0) disables this timer, with the extension waiting for a database server response indefinitely. Visible only when “Advanced“ is selected. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
User Defined Metric | Choice | Enables the creation of a user-defined metric. The metric value is calculated based on the result set returned as a result of the SQL Script execution. Available options are as follows:
| Introduced in 2.0.0 |
Metric Name Suffix | Text | The metric name suffix. The resulting metric name is ue.sqlodbc.user.<metric_suffix> Visible only and mandatory when User Defined Metric = “Counter”. | Introduced in 2.0.0 |
Column For Metric Value Calculation | Text | The result set’s column from which the metric value shall be retrieved. If provided, the metric value is incremented by the value of this column. Otherwise, the metric value is incremented by one for each row of the result set. Note that the configured column should represent always a number. Visible only when User Defined Metric = “Counter”. | Introduced in 2.0.0 |
Metric Attributes | Choice | Define the metric attributes selection method. Available options are as follows:
When --None-- is selected, no attributes are sent when metric values are published. When “Column Based” is selected, the metric attribute names are taken from the result set’s columns, and their values are taken from the row values of the result set. Visible only when User Defined Metric = “Counter”. | Introduced in 2.0.0 |
Column List | Text | Comma-separated list of result set’s columns to be used as attributes. Visible only and mandatory when Metric Attributes = “Column Based“. At least one column name should be selected | Introduced in 2.0.0 |
Output Fields
| Field | Type | Description | Version Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execution Time | Float | The execution time of the query is in seconds. | Introduced in 1.0.0 |
Environment Variables
Variable: UE_EXTENSION_OUTPUT_MAX_SQL_ROWS
Exit Codes
Extension Exit Code | Status | Status Description | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Success | “Task executed successfully.“ | Successful Execution |
1 | Failed | “Execution Failed: <<Error Description>>” | This extension error is mapped to the following cases:
|
20 | Failed | “Data Validation Error: <<Error Description>>“ | Input fields validation error.** See STDERR for more detailed error descriptions. |
29 | Failed | “File Write Error: <<Error Description>>“ | Failed to write SQL script results to the target file. |
STDOUT and STDERR
STDOUT and STDERR provide additional information to the user.
Observability
Metric: ue.sqlodbc.sql.rows
This metric is created based on the respective Event Template.
Name | Instrument Type | Unit (UCUM) | Attributes | Instrumented By | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histogram | {row} | As defined in metric attributes. | Universal Controller | Measures the total rows affected by the executed SQL statement(s). The metric value is aggregated across different task instances |
Note: When row counts are reported as a -1 from ODBC drivers, from a metric point of view they are considered equal to zero.
Metric: ue.sqlodbc.sql.duration
This metric is created based on the respective Event Template.
Name | Instrument Type | Unit (UCUM) | Attributes | Instrumented By | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histogram | s | As defined in metric attributes. | Universal Controller | Duration of the given SQL statements to be executed. This is measured from the client side and includes network delays. The metric value is aggregated across different task instances |
Metric Attributes
The following attributes are applicable for ue.sqlodbc.sql.rows and ue.sqlodbc.sql.duration metrics.
Attribute Name | Enabled | Description |
|---|---|---|
action | By Default | The selected action of the Universal Task. |
script | Optionally | The name of the SQL script that is executed. |
dsn | By Default | The DSN is used for the database. |
dbname | By Default | The name of the database. |
dbaddress | By Default | The host address of the database. |
dbsystem | By Default | The system type of the database. |
Optional Metric Attributes
In the table above some Attributes are optionally enabled. Those attributes are not activated by default, cause it might lead to high cardinality scenarios in case the distinct values of those attributes used for a customer installation are too many. Administrators can activate them with caution as follows:
Go to Administration → Universal Templates
Select the Universal Template
Click “Event Templates” Tab
Select the Name of the Event Template you want to update, which represents the metric you are interested in.
Update the “Metric Label Attributes” Field by adding the required Attribute Name.
User Defined Metrics
This integration enables users to create their own metrics based on the result set’s data.
Name | Instrument Type | Unit (UCUM) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ue.sqlodbc.user.<user-defined metric suffix> | Counter | - | A counter representing an entity derived by the result set data. |
Attributes are controlled by the field Column List when MetricAttributes = “Column Based“. Some representative configuration examples are listed below where it is assumed that an Oracle database is used and a database table named car_sales exists and holds car sales data.
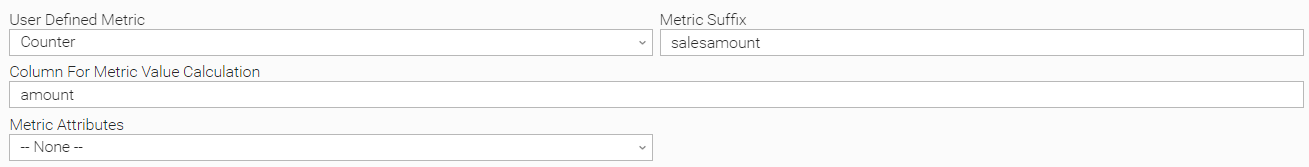
Example: Add 1 for every row
Let’s assume that car sales data is being retrieved from an SQL statement. An example could be the following.
select * from car_sales where sales_date between TRUNC(SYSDATE-1) and TRUNC(SYSDATE)
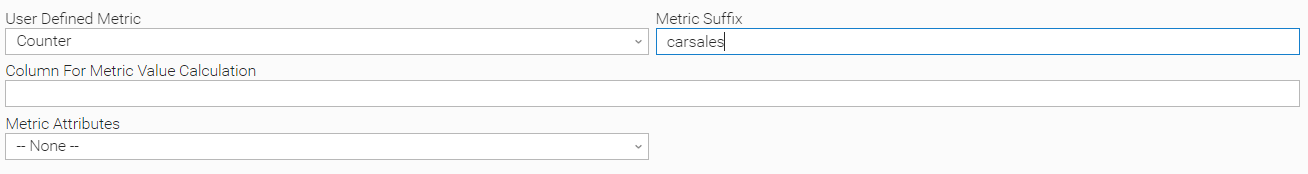
The task author wants to take the number of sales of the previous day and push them as a metric. For that, instrumentation is required to be added on top of the existing SQL statement as follows:
The above setup will create a metric called ue.sqlodbc.user.carsales and for each entry on the result set, the value of 1 will be added to the metric.
Example: Add a selected value for every row
Let’s assume that the same table is being selected to retrieve car sales amounts. An example could be the following:
select amount, sales_date, car_make, car_model from car_sales where sales_date between TRUNC(SYSDATE-1) and TRUNC(SYSDATE)
The task author wants to calculate the total sales amount of the previous day and push the value as a metric. For that instrumentation is required to be added on top of the existing SQL statement.
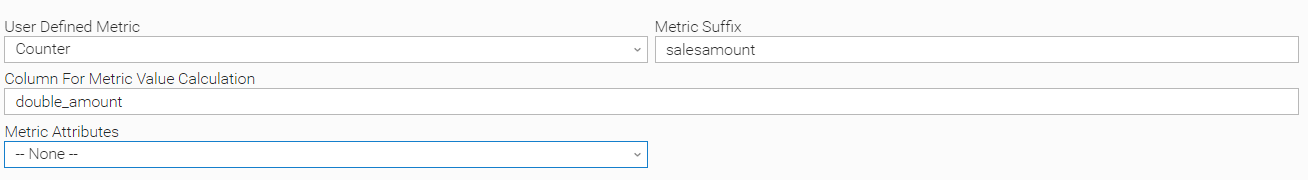
The above setup will create a metric called ue.sqlodbc.user.sales amount and for each entry on the result set, the value of the column amount will be added to the metric. A second example is shown below where the amount is manipulated on the select statement.
select amount*2 as double_amount, sales_date, car_make, car_model from car_sales where sales_date between TRUNC(SYSDATE-1) and TRUNC(SYSDATE)
In that case, the configuration of the metric could be the following. As shown, the virtual column named double_amount is used as a parameter of the field Column For Metric Value Calculation.
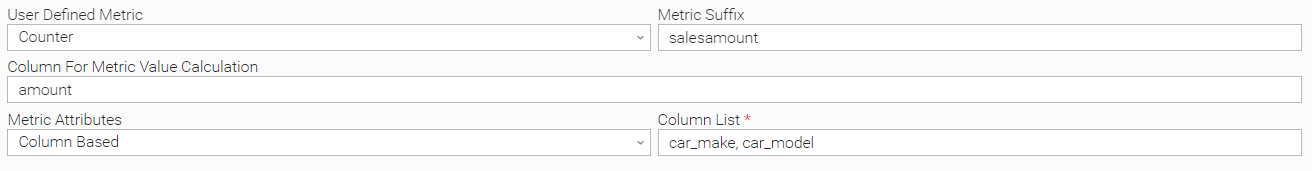
Example: Using attributes for labeling data
Attributes and their values put extra information with respect to the published metric. Based on the example before, if the task author would require to see the sales amount per car_make and car_model then the required configuration would be the following:
Other Observability Configuration Options
Administrators can update the Universal Event Template to control additional attributes that can be sent out for Universal Event-based Metrics. However, this configuration should be approached with caution. When the possible distinct values of those attributes are high, that might lead to high cardinality issues.
Administrators can activate them with caution as follows:
Go to Administration → Universal Templates
Select the Universal Template
Click “Event Templates” Tab
Select the Name of the Event Template you want to update, which represents the metric you are interested in.
Update the “Optional Metric Labels” List the required Metric Labels.
How To
Import Universal Template
To use the Universal Template, you first must perform the following steps.
This Universal Task requires the Resolvable Credentials feature. Check that the Resolvable Credentials Permitted system property has been set to true.
To import the Universal Template into your Controller, follow these instructions.
When the files have been imported successfully, refresh the Universal Templates list; the Universal Template will appear on the list.
Modifications of this integration, applied by users or customers, before or after import, might affect the supportability of this integration. For more information refer to Integration Modifications.
Configure Universal Task
For a new Universal Task, create a new task, and enter the required input fields.
Import Grafana Dashboard
Users can benefit from a ready-to-use sample dashboard that this downloadable integration offers when observability features are used. It is located under /observability/grafana/ directory inside the downloadable zip file from Stonebranch Integration Hub. Administrators should refer to the official Grafana User Guide on how to import a Grafana Dashboard.
Dashboard’s Prometheus data source is configured as a variable and thus needs to be mapped to an existing Data Source configured on the target Grafana instance.
Integration Modifications
Modifications applied by users or customers, before or after import, might affect the supportability of this integration. The following modifications are discouraged to retain the support level as applied for this integration.
Python code modifications should not be done.
Template Modifications
General Section
"Name", "Extension", "Variable Prefix", and "Icon" should not be changed.
Universal Template Details Section
"Template Type", "Agent Type", "Send Extension Variables", and "Always Cancel on Force Finish" should not be changed.
Result Processing Defaults Section
Success and Failure Exit codes should not be changed.
Success and Failure Output processing should not be changed.
Fields Restriction Section
The setup of the template does not impose any restrictions, However with respect to the "Exit Code Processing Fields" section.Success/Failure exit codes need to be respected.
In principle, as STDERR and STDOUT outputs can change in follow-up releases of this integration, they should not be considered as a reliable source for determining the success or failure of a task.
Event Template configuration when related to “Metric Label Attributes” & “Optional Metric Labels” is allowed. However, administrators should be cautious of high cardinality scenarios that might occur.
Users and customers are encouraged to report defects, or feature requests at Stonebranch Support Desk.
Document References
This document references the following documents:
Document Link | Description |
|---|---|
User documentation for creating, working with, and understanding Universal Templates and Integrations. | |
User documentation for creating Universal Tasks in the Universal Controller user interface. |
Known Issues
The use of FILE Data Source Names (FILEDSN) for connecting to an Oracle database is not supported in this version. Attempting to establish a connection using a FILE DSN may result in unexpected behavior or errors, as it is not proven not to be reliable with the latest ODBC Driver.
The use of environmental variables to determine the location of the DSN file during “Data Source Name” Choice Field Execution
Changelog
ue-sql-odbc 3.0.1 (2024-11-14)
Enhancements
Fixed: Refined database message handling (#42058, #42059).Fixed: Resolved issue which would occasionally cause values of consecutively published events to be incorrectly mapped (#42830).
ue-sql-odbc 3.0.0 (2024-04-11)
Deprecations and Breaking Changes
Breaking Change:Bundle dependent librarypyodbcwithin integration. Supported UAC Versions are now 7.4.0.0 and later (#36330).
ue-sql-odbc 2.2.0 (2023-12-21)
Enhancements
Added: Provide the capability to enable or disable the auto-commit mechanism for MS SQL Server databases. (#35223).
ue-sql-odbc 2.1.0 (2023-11-09)
Enhancements
Added: Official support for the Amazon Redshift Database (#34719).Added: New Choice Field “SQL Source” that gives the opportunity to provide the SQL Script either as a UAC Script or as plain text (#34606).Added: Enhanced security when the Connection Method is “Connection String” by selecting the proper Credential and passing it via the connection string. This can be achieved using the following notation:[credential_name].userand[credential_name].password (#34605).
Fixes
Fixed: Authenticate with the system user connectivity issue when the Connection Method is “Connection String” and the Database Type is “MSSQL” (#34623).
ue-sql-odbc 2.0.0 (2023-10-07)
Enhancements
Added: Observability through Metrics related to SQL execution metadata (#34187).Added: Observability through User-Defined Metrics based on SQL resultset (#34220).Added: Feature added to protect task authors from pushing into Universal Controller unnecessary database data by providing the capability to control the number of lines from the SQL result set that will be available on extension output. Task Authors can use UE_EXTENSION_OUTPUT_MAX_SQL_ROWS environment variable to control the behavior (#33848)
Deprecations and Breaking Changes
Breaking Change:Updated the status descriptions to be more informative (#34335).Tasks or workflows evaluating the "Status Description" of the task Instance, either programmatically or within UAC, might be affected by it. In that case, they need to conform to the new "Status Description" Text
Breaking Change:Compatibility of this integration for Universal Controller and Universal Agent changed from ">=7.1" to ">=7.2". Template flag “Send Extension Variables” is used which is available starting from Universal Controller 7.2.0.0 (#34187).Breaking Change:In this version, by default, the returned datasets displayed on the extension output are truncated to the first 100 rows. If more than 100 rows need to be pushed into the extension output, the environment variable UE_EXTENSION_OUTPUT_MAX_SQL_ROWS needs to be set appropriately on the task definition.(#33848).Breaking Change:Extension Invocation Fields > Credential fields are displayed as an object for better readability
ue-sql-odbc 1.0.0 (2023-06-29)
Initial Version